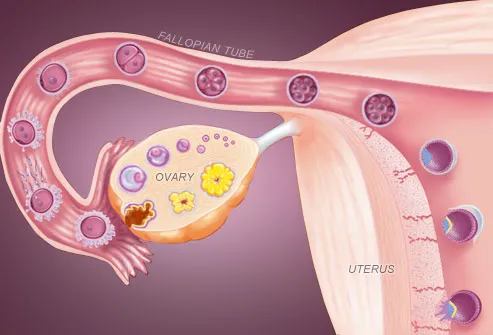
A woman can get pregnant if a man’s sperm reaches one of her eggs (ova). Contraception tries to stop this happening by keeping the egg and sperm apart or by stopping egg production. One method of contraception is female sterilisation.
Female sterilisation is usually carried out under general anaesthetic but can be carried out under local anaesthetic, depending on the method used. The surgery involves blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes, which link the ovaries to the womb (uterus).
This prevents the woman’s eggs from reaching sperm and becoming fertilised. Eggs will still be released from the ovaries as normal, but they will be absorbed naturally into the woman's body.
At a glance: facts about female sterilisation
-
In most cases, female sterilisation is more than 99% effective, and only one woman in 200 will become pregnant in her lifetime after having it done.
-
You don't have to think about it every day, or every time you have sex, so it doesn't interrupt or affect your sex life.
-
Sterilisation can be performed at any time during the menstrual cycle. It won't affect hormone levels.
-
You'll still have periods after being sterilised.
-
You will need to use contraception until the operation is done and until your next period or for three months afterwards (depending on the type of sterilisation).
-
As with any surgery, there's a small risk of complications. These include internal bleeding, infection or damage to other organs.
-
There's a small risk that the operation won't work. Blocked tubes can rejoin immediately or years later.
-
If the operation fails, this may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy (when a fertilised egg implants outside the womb, usually in a fallopian tube).
-
The sterilisation operation is difficult to reverse.
-
Female sterilisation doesn't protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), so always use a condom to protect yourself and your partner against STIs.
How female sterilisation works
Female sterilisation works by preventing eggs from travelling down the fallopian tubes. This means a woman's eggs cannot meet sperm, and fertilisation cannot happen.
How female sterilisation is carried out
There are two main types of female sterilisation:
-
when your fallopian tubes are blocked, for example with clips or rings (tubal occlusion)
-
when implants are used to block your fallopian tubes (hysteroscopic sterilisation, or HS)
It can be a fairly minor operation, with many women returning home the same day. Sterilisation is usually carried out using tubal occlusion (blocking the fallopian tubes).
Tubal occlusion
First, your surgeon will need to access and examine your fallopian tubes, using either laparoscopy or mini-laparotomy.
A laparoscopy is the most common method of accessing the fallopian tubes. The surgeon makes a small cut in your abdominal wall near your belly button and inserts a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a small flexible tube that contains a tiny light and camera. The camera relays images of the inside of your body to a television monitor. This allows the surgeon to see your fallopian tubes clearly.
A mini-laparotomy involves a small incision, usually less than 5cm (2 inches), just above the pubic hairline. Your surgeon can then access your fallopian tubes through this incision.
A laparoscopy is usually the preferred option because it is faster. However, a mini-laparotomy may be recommended for women who:
-
have had recent abdominal or pelvic surgery
-
are obese (have a body mass index of 30 or over)
-
have a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (a bacterial infection that can affect the womb and fallopian tubes)
Blocking the tubes
The fallopian tubes can be blocked using one of the following methods:
-
applying clips – plastic or titanium clamps are closed over the fallopian tubes
-
applying rings – a small loop of the fallopian tube is pulled through a silicone ring, then clamped shut
-
tying and cutting the tube – this destroys 3-4cm (1–1.5 inches) of the tube
-
Hysteroscopic sterilisation (fallopian implants)
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has published guidance about hysteroscopic sterilisation. However, the technique is not yet widely available.
The implants are usually inserted under local anaesthetic, and the procedure doesn't require cuts to be made in your abdomen. You may also be given a sedative to relax you.
A narrow tube with a telescope at the end, called a hysteroscope, is passed through your vagina and cervix. A guidewire is used to insert a tiny piece of titanium metal (called a microinsert) into the hysteroscope, then into each of your fallopian tubes. This means that the surgeon does not need to cut into your body.
The implant causes the fallopian tube to form scar tissue around it, which eventually blocks the tube.
You should carry on using contraception until an imaging test has confirmed that your fallopian tubes are blocked. This can be done with one or more of the following:
-
a hysterosalpingogram (HSG) – a type of X-ray that is taken after a special dye has been injected to show up any blockages in your fallopian tubes
-
a hysterosalpingo-contrast-sonography (HyCoSy) – a type of ultrasound scan involving injecting dye into your fallopian tubes
Removing the tubes (salpingectomy)
If blocking the fallopian tubes has been unsuccessful, the tubes may be completely removed. Removal of the tubes is called salpingectomy.
Before the operation
Your GP will strongly recommend counselling before referring you for sterilisation. Counselling will give you a chance to talk about the operation in detail, and talk about any doubts, worries or questions that you might have.
If you decide to be sterilised, your GP will refer you to a specialist for treatment. This will usually be a gynaecologist at your nearest NHS hospital. A gynaecologist is a specialist in the female reproductive system.
If you choose to have a sterilisation, you will be asked to use contraception until the day of the operation, and to continue using it:
-
until your next period if you are having your fallopian tubes blocked (tubal occlusion)
-
for around three months if you are having fallopian implants (hysteroscopic sterilisation)
Sterilisation can be performed at any stage in your menstrual cycle.
Before you have the operation you will be given a pregnancy test to make sure that you are not pregnant. It is vital to know this because once the surgeon blocks your fallopian tubes there is a high risk that any pregnancy will become ectopic (when the fertilised egg grows outside the womb, usually in the fallopian tubes). An ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening because it can cause severe internal bleeding.
Recovering after the operation
Once you have recovered from the anaesthetic, passed urine and had something to eat, you will be allowed home. If you leave hospital within hours of the operation, ask a relative or friend to pick you up, or take a taxi.
The healthcare professionals treating you in hospital will tell you what to expect and how to care for yourself after surgery. They may give you a contact number to call if you have any problems or any questions.
If you have had a general anaesthetic, do not drive a car for 48 hours afterwards. This is because even if you feel fine, your reaction times and judgement may not be back to normal.
How you will feel
It is normal to feel unwell and a little uncomfortable for a few days if you have had a general anaesthetic, and you may have to rest for a couple of days. Depending on your general health and your job, you can normally return to work five days after tubal occlusion. However, you should avoid heavy lifting for about a week.
You may have some slight vaginal bleeding. Use a sanitary towel rather than a tampon until this has gone. You may also feel some pain, similar to period pain. You may be prescribed painkillers for this. If the pain or bleeding gets worse, seek medical attention.
Caring for your wound
If you had tubal occlusion to block your fallopian tubes, you will have a wound with stitches where the surgeon made an incision (cut) into your abdomen. Some stitches are dissolvable and disappear on their own, and some will need to be removed. If your stitches need removing you will be given a follow-up appointment for this.
If there is a dressing over your wound, you can normally remove this the day after your operation. After this, you will be able to have a bath or shower as normal.
Having sex
Your sex drive and enjoyment of sex will not be affected. You can have sex as soon as it is comfortable to do so after the operation.
If you had tubal occlusion, you will need to use contraception until your first period to protect yourself from pregnancy.
If you had hysteroscopic sterilisation, you will need to use another form of contraception for around three months after surgery. After scans have confirmed that the implants are in the correct position, you will no longer need contraception.
Sterilisation will not protect you from sexually transmitted infections, so continue to use barrier contraception such as condoms if you are unsure of your partner's sexual health.
Who can have it done?
Almost any woman can be sterilised. However, sterilisation should only be considered by women who do not want any more children, or do not want children at all. Once you are sterilised it is very difficult to reverse the process, so it's important to consider the other options available before making your decision. Sterilisation reversal is not usually available on the NHS.
Surgeons are more willing to perform sterilisation when women are over 30 years old and have had children, although some younger women who have never had a baby choose it.
Advantages and disadvantages of female sterilisation
Advantages
-
female sterilisation can be more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy
-
tubal occlusion (blocking the fallopian tubes) and removal of the tubes (salpingectomy) should be effective immediately – however, doctors strongly recommend that you continue to use contraception until your next period
-
hysteroscopic sterilisation is usually effective after around three months – research collected by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) found that the fallopian tubes were blocked after three months in 96% of sterilised women
Other advantages of female sterilisation are that:
-
there are rarely any long-term effects on your sexual health
-
it will not affect your sex drive
-
it will not affect the spontaneity of sexual intercourse or interfere with sex (as other forms of contraception can)
-
it will not affect your hormone levels
Disadvantages
-
female sterilisation does not protect you against sexually transmitted infections so you should still use a condom if you are unsure about your partner's sexual health
-
it is very difficult to reverse a tubal occlusion – this involves removing the blocked part of the fallopian tube and rejoining the ends, and reversal operations are rarely funded by the NHS
Risks
-
with tubal occlusion there is a very small risk of complications, including internal bleeding and infection or damage to other organs
-
it is possible for sterilisation to fail – the fallopian tubes can rejoin and make you fertile again, although this is rare (about 1 in 200 women become pregnant in their lifetime after being sterilised)
-
if you do get pregnant after the operation, there is an increased risk that it will be an ectopic pregnancy (when the fertilised egg grows outside the womb, usually in the fallopian tubes)
If you miss a period, take a pregnancy test immediately. If the pregnancy test is positive, you must see your GP so that you can be referred for a scan to check if the pregnancy is inside or outside your womb.
With hysteroscopic sterilisation, there is a small risk of pregnancy even after your tubes have been blocked. Research collected by NICE has shown that possible complications after fallopian implants can include:
-
pain after the operation – in one study, nearly eight out of 10 women reported pain afterwards
-
the implants being inserted incorrectly – this affected two out of 100 women
-
bleeding after the operation – many women had light bleeding after the operation, and nearly a third had bleeding for three days
Contraception services are free and confidential, including for people under the age of 16.
If you're under 16 and want contraception, the doctor, nurse or pharmacist won't tell your parents (or carer) as long as they believe you fully understand the information you're given and your decisions. Doctors and nurses work under strict guidelines when dealing with people under 16. They'll encourage you to consider telling your parents, but they won't make you. The only time that a professional might want to tell someone else is if they believe you're at risk of harm, such as abuse. The risk would need to be serious, and they would usually discuss this with you first.